RDM-Basics
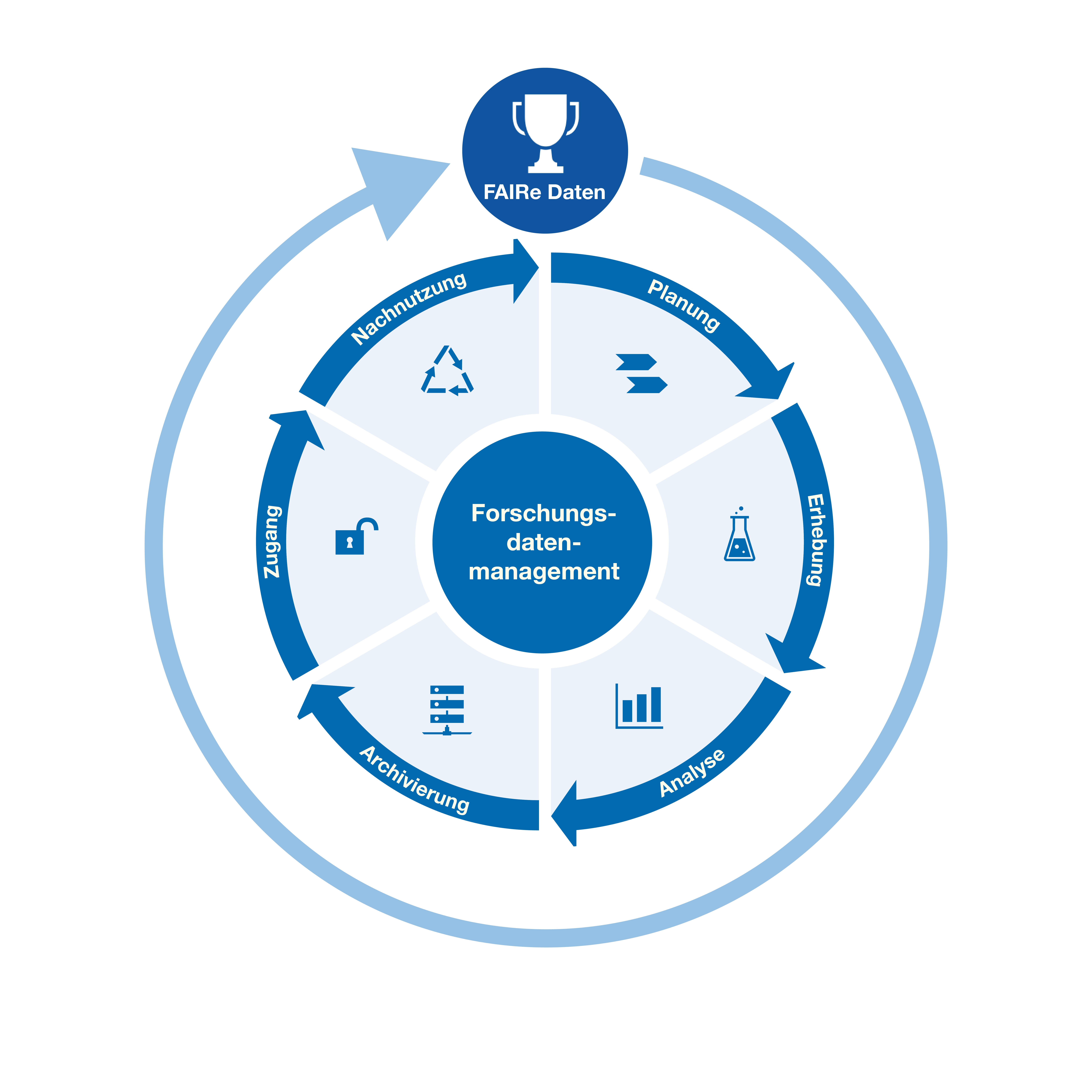
Research Data Management (RDM) is relevant across all areas of research. A successful RDM starts at all points within the research data life cycle (see figure). Thus, RDM is just as relevant in the planning of a project, in the collection of data as well as their analysis, as it is during archiving and access for subsequent use. At first glance, RDM means more time and effort for researchers, so that many often hesitate to apply it. However, to see the benefits of good RDM, many advantages should be taken into account:
- Reusability of research data and metadata even after the end of a project.
- Adherence to FAIR principles.
- Collecting all necessary data and metadata for subsequent publication.
- Enabling collaborative work.
- Early consideration of and compliance with data security criteria.
- Enabling reproducibility through increased visibility of (meta)data.
- Consideration of DFG guidelines on good scientific practice.
- Faster and easier application for funding.
- And last but not least: Using RDM tools like Coscine makes implementation even easier ;)